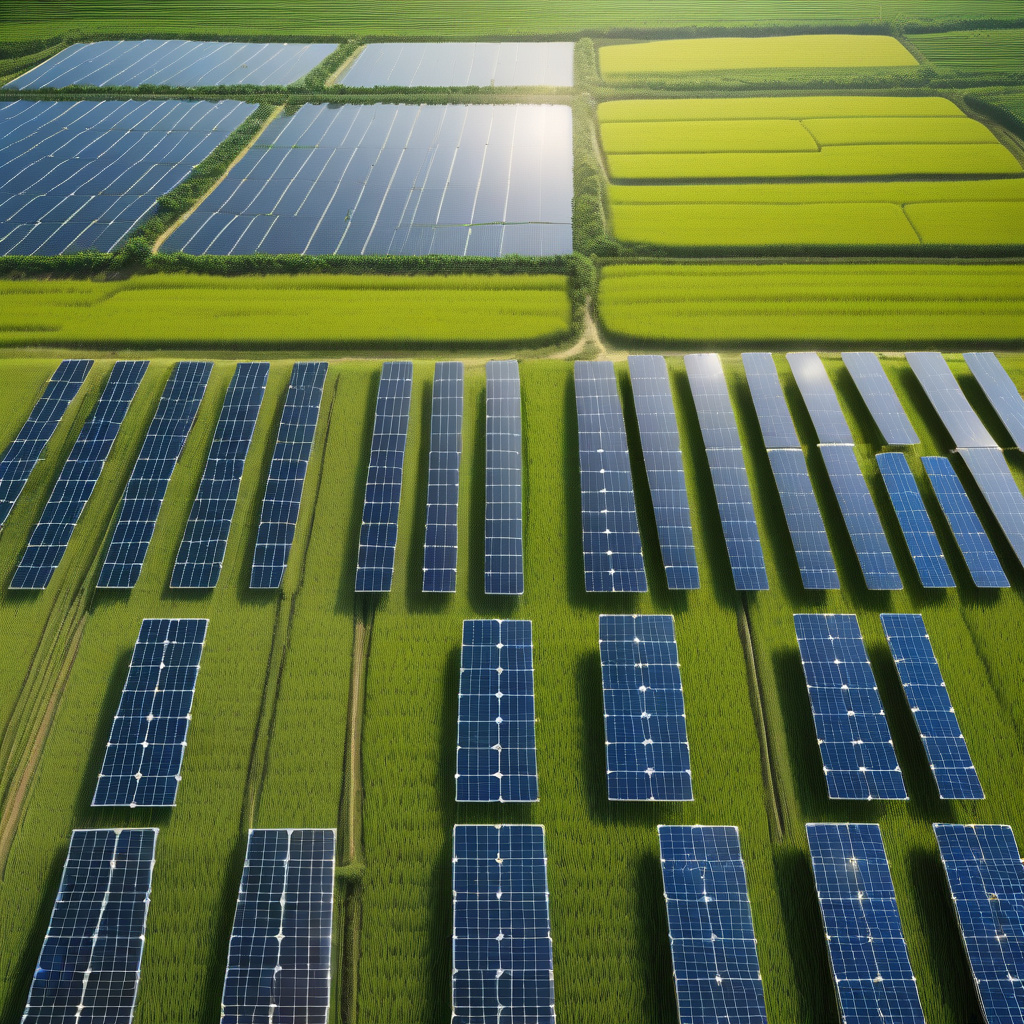
Solar panels above rice paddies generate power while preserving crop yields
Japan may have found a way to harvest renewable electricity without giving up valuable farmland. By installing solar panels above rice paddies, the country is not only generating power but also preserving its crucial crop yields. This innovative approach is a win-win solution that showcases the power of sustainable technology in agriculture.
Traditionally, solar panels are installed on rooftops or in large open fields, taking up space that could otherwise be used for agriculture. However, by placing these panels above rice paddies, Japan is utilizing the vertical space without compromising the productivity of the land below. This method, known as agrivoltaics, allows for dual land use, maximizing the efficiency of both energy production and crop cultivation.
One of the key advantages of incorporating solar panels above rice paddies is the reduction of water evaporation. The panels provide shade, which helps to decrease the amount of water lost through evaporation, leading to water savings for farmers. This is especially significant in regions where water resources are scarce, highlighting the potential of agrivoltaics to promote water conservation in agriculture.
Moreover, the presence of solar panels above rice paddies can create a microclimate that benefits crop growth. The shade from the panels can help regulate temperature and humidity levels, creating a more stable environment for the rice plants. Additionally, the panels can act as a barrier against heavy rainfall, protecting the crops from potential damage during storms.
In terms of energy generation, the solar panels above rice paddies are producing clean and renewable electricity. This not only reduces the reliance on fossil fuels but also contributes to the fight against climate change by lowering carbon emissions. Japan’s initiative to combine renewable energy production with agricultural practices sets a positive example for other countries looking to implement sustainable solutions.
Furthermore, the dual-use nature of agrivoltaics can potentially increase the overall productivity of the land. By generating electricity on-site, farmers can power their operations more sustainably, reducing costs and reliance on external sources. This integrated approach to farming and energy production demonstrates the possibilities of innovation in addressing both food security and clean energy needs.
As the world faces the challenges of climate change and food security, solutions like solar panels above rice paddies offer a glimpse into a more sustainable future. By harnessing the power of the sun above agricultural fields, countries can meet their energy demands while safeguarding precious farmland. Japan’s pioneering efforts in agrivoltaics underscore the importance of thinking creatively and holistically when addressing the interconnected issues of energy, agriculture, and the environment.
In conclusion, the integration of solar panels above rice paddies represents a harmonious blend of technology and agriculture, showcasing the potential for innovation in sustainable practices. By reimagining the use of land for both energy generation and crop cultivation, Japan is leading the way towards a more resilient and environmentally conscious future.
solar energy, agriculture, sustainability, innovation, Japan