361,000-year-old Discovery in China: Oldest Wooden Tools Shake Up Archaeology
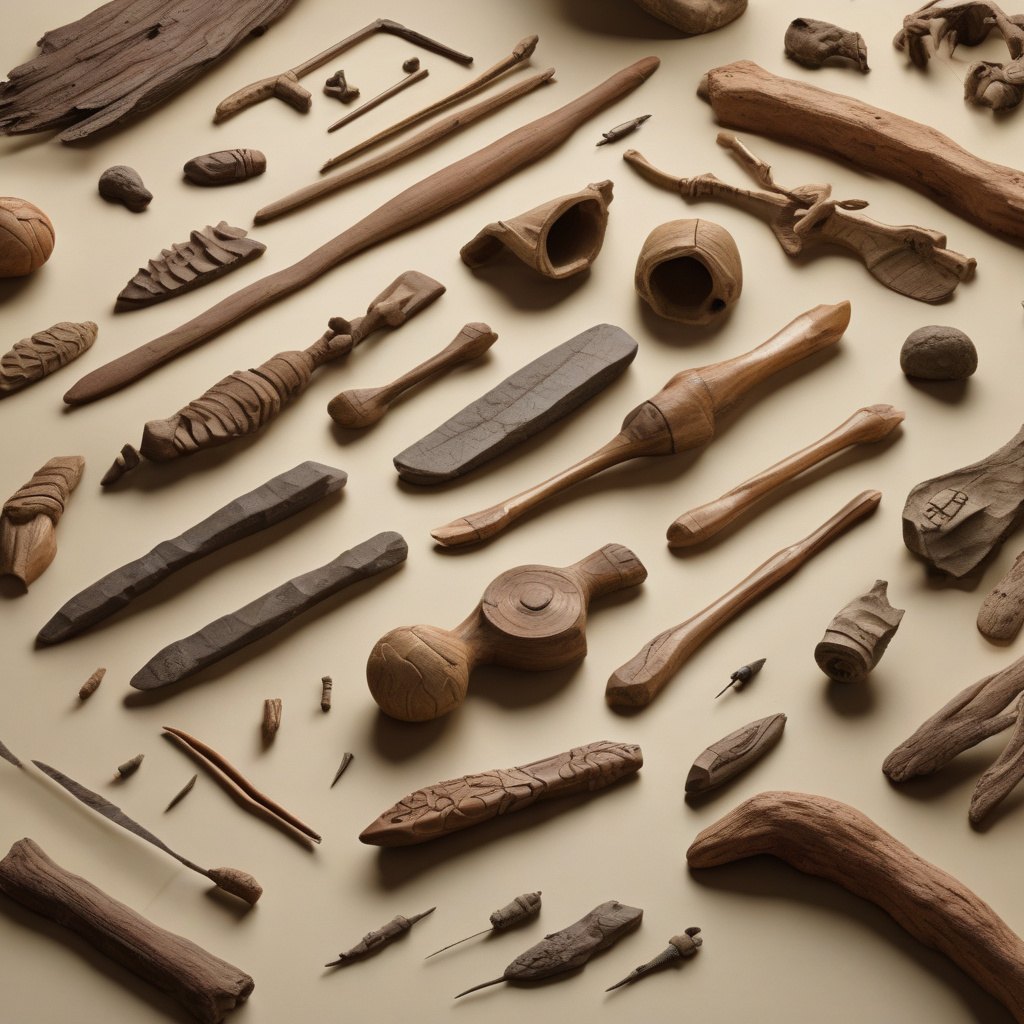
Researchers in China have unearthed the oldest complex wooden technology at the Paleolithic site of Shangchen. This groundbreaking discovery dates back an astonishing 361,000 years, pushing the boundaries of what we know about early human innovation and craftsmanship. The find includes six wooden tools, such as a hand drill, which showcase the remarkable skills of our ancient ancestors. This revelation not only sheds light on the cognitive abilities of early humans but also challenges existing beliefs about the timeline of technological development.
The excavation at Shangchen has provided archaeologists with a rare glimpse into the lives of our prehistoric counterparts. The sophistication of the wooden tools suggests a level of dexterity and problem-solving capabilities that were previously underestimated. This finding forces a reevaluation of the cognitive and technological capacities of early humans, indicating that their skills were far more advanced than previously thought.
Moreover, the discovery of these ancient wooden tools poses intriguing questions about the migration patterns and cultural exchanges of early human populations. The intricate nature of the artifacts implies a level of societal organization and knowledge transfer that was previously unrecognized. It suggests that these early humans were capable not only of creating complex tools but also of passing down this knowledge within and across generations.
The implications of this discovery extend far beyond the field of archaeology. They offer a unique opportunity to reflect on the ingenuity and resilience of the human species throughout history. The ability to craft functional tools from wood, a material that is prone to decay, showcases the resourcefulness and adaptability of early humans in the face of environmental challenges.
Furthermore, the find at Shangchen highlights the importance of preserving and exploring archaeological sites to uncover the hidden treasures of our past. It underscores the critical role that research and excavation play in expanding our understanding of human history and evolution. By investing in such endeavors, we not only unravel the mysteries of our origins but also gain valuable insights that can inform contemporary innovation and technology.
In conclusion, the discovery of the 361,000-year-old wooden tools at Shangchen represents a significant milestone in the field of archaeology. It challenges conventional wisdom about the capabilities of early humans and provides a new perspective on the ingenuity of our ancestors. This finding serves as a testament to the enduring legacy of human creativity and adaptability, inspiring us to continue exploring the depths of our past to unlock the secrets of our shared heritage.
archaeology, technology, innovation, humanhistory, ancientcraftsmanship