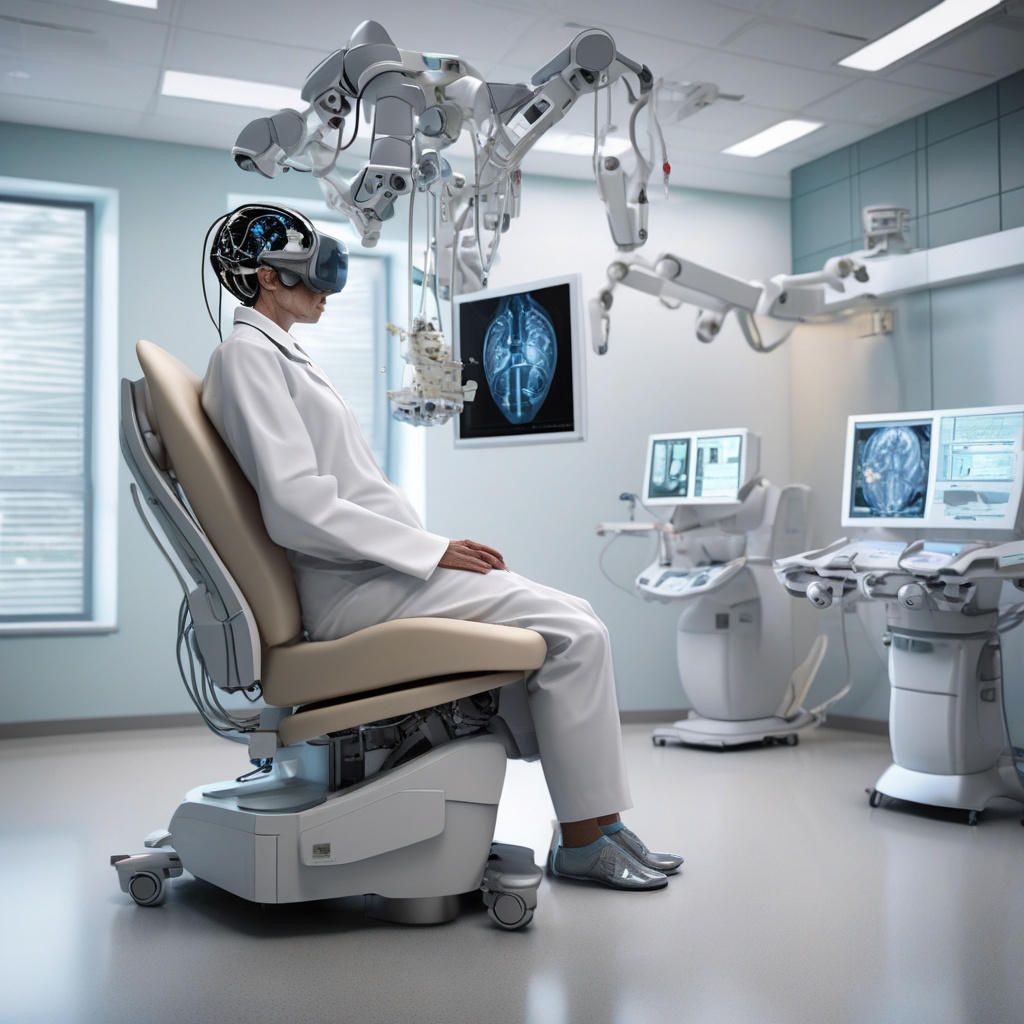
AI-powered brain chips let paralyzed patients steer robot arm with thoughts
A new wearable, noninvasive brain-computer interface (BCI) system that uses artificial intelligence has been designed to revolutionize the lives of paralyzed patients. This groundbreaking technology allows individuals with paralysis to control a robotic arm through the power of their thoughts, offering newfound independence and freedom.
Imagine the impact this innovation could have on the daily lives of those who have lost the ability to move or communicate due to spinal cord injuries or neurological disorders. Tasks that were once impossible become achievable with this cutting-edge technology. From feeding themselves to interacting with their environment, paralyzed individuals now have the opportunity to regain control and autonomy.
The AI-powered brain chips work by interpreting the user’s brain signals and translating them into commands that the robotic arm can understand and execute. Through a series of sensors placed on the scalp, the system detects the user’s intent and moves the robotic arm accordingly. This seamless integration of human intent and machine movement is a remarkable feat of engineering and artificial intelligence.
One of the key advantages of this BCI system is its noninvasive nature. Unlike previous brain-computer interfaces that required surgical implantation of electrodes, this wearable device sits comfortably on the user’s head, making it accessible and user-friendly. This advancement opens up the technology to a wider range of patients and eliminates the risks associated with invasive procedures.
Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence into the system enhances its capabilities and adaptability. The AI algorithms learn and adapt to the user’s brain signals over time, improving the accuracy and responsiveness of the robotic arm. This personalized approach ensures a seamless interaction between the user and the technology, creating a more natural and intuitive user experience.
The implications of this technology extend beyond individual patients to the field of healthcare as a whole. By pushing the boundaries of what is possible in assistive technology, researchers and developers are paving the way for future innovations in patient care and rehabilitation. The potential for AI-powered brain chips to improve the quality of life for paralyzed individuals is immense and holds promise for transforming the way we approach disability and assistive technologies.
As we look to the future, it is clear that advancements in AI and neuroscience will continue to drive progress in the field of brain-computer interfaces. The collaboration between human ingenuity and technological innovation has the power to reshape the lives of individuals with disabilities and open up new possibilities for human-machine interaction. The era of mind-controlled robotics is no longer a distant dream but a tangible reality, offering hope and empowerment to those who need it most.
In conclusion, the development of AI-powered brain chips that allow paralyzed patients to control a robotic arm with their thoughts represents a significant leap forward in assistive technology. This innovative system not only restores a sense of agency and independence to individuals with paralysis but also showcases the transformative potential of artificial intelligence in healthcare. As we witness the impact of this technology on the lives of patients, we are reminded of the boundless possibilities that arise when human creativity and technological innovation converge.
AI, BrainChips, ParalyzedPatients, Robotics, AssistiveTechnology