By immersing users in a computer-generated environment, VR offers unique opportunities for athletes, coaches, and fans alike. The integration of VR into sports is not merely a trend; it represents a significant shift in how training, performance analysis, and fan engagement are approached.
As the technology continues to evolve, its applications within the sports industry are becoming increasingly sophisticated, leading to enhanced performance and richer experiences. The adoption of VR in sports can be traced back to its initial use in training simulations for pilots and military personnel. However, its potential was quickly recognized by sports professionals who saw the opportunity to replicate game scenarios and improve decision-making skills.
Today, VR is being utilized by professional teams and organizations across various sports, from football to basketball, and even in individual sports like tennis and golf. This technology not only aids in skill development but also provides a platform for mental conditioning, allowing athletes to visualize and rehearse their performances in a controlled environment.
Key Takeaways
- Virtual reality (VR) is revolutionizing the sports industry by providing immersive and interactive experiences for athletes, fans, and marketers.
- Athletes are using VR technology for training purposes, allowing them to simulate game scenarios and improve their skills in a safe and controlled environment.
- VR is enhancing the fan experience by offering 360-degree views of games, behind-the-scenes access, and interactive content, creating a more engaging and personalized experience for viewers.
- The advantages of VR in sports training include improved performance, reduced risk of injury, and the ability to analyze and track player movements and techniques.
- Despite its potential, VR in sports faces challenges such as high costs, technical limitations, and the need for further research and development.
Virtual Reality Training for Athletes
One of the most significant applications of virtual reality in sports is its use in training athletes. Traditional training methods often involve repetitive drills and physical practice, which can be time-consuming and may not always replicate real-game scenarios.
For instance, quarterbacks in American football can practice their passing techniques by throwing virtual footballs to receivers running routes in a simulated game environment. This immersive experience helps athletes refine their skills without the physical toll of on-field practice. Moreover, VR training can be tailored to meet the specific needs of individual athletes.
Coaches can design scenarios that focus on particular skills or strategies, enabling athletes to work on their weaknesses in a safe and controlled setting. For example, a basketball player might use VR to practice shooting under pressure by simulating game situations where they must make critical shots with defenders closing in. This personalized approach not only enhances skill acquisition but also builds confidence as athletes become more familiar with high-pressure situations.
Enhancing Fan Experience with Virtual Reality
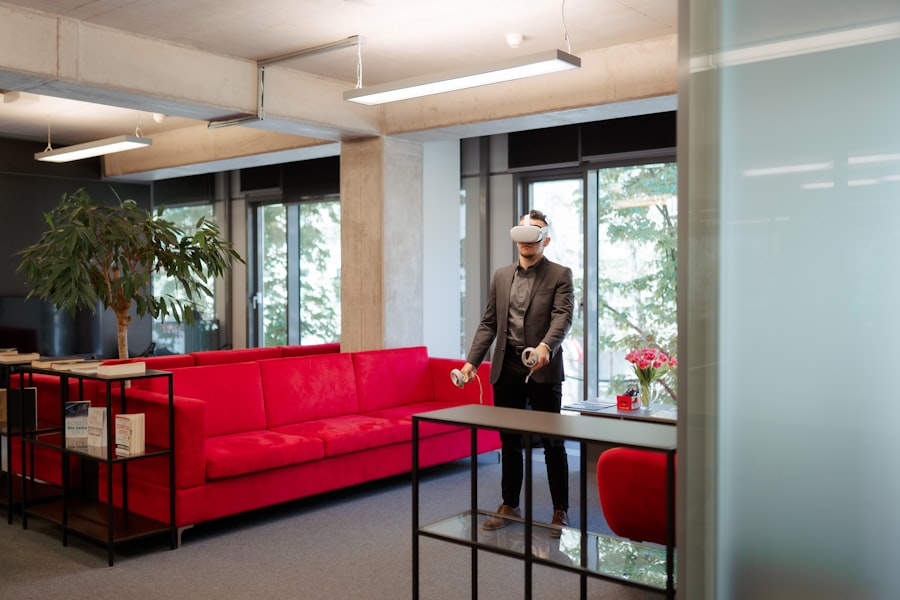

The impact of virtual reality extends beyond the training ground; it also revolutionizes the way fans engage with their favorite sports. VR technology allows fans to experience games from unique perspectives that were previously unattainable. For instance, through VR headsets, fans can enjoy a front-row seat at a live game or even feel as if they are on the field with the players.
This immersive experience creates a deeper emotional connection between fans and their teams, enhancing loyalty and engagement. In addition to live game experiences, VR can also provide fans with interactive content that enriches their understanding of the sport. For example, virtual reality can be used to create behind-the-scenes tours of stadiums or training facilities, offering fans an insider’s view of their favorite teams.
Furthermore, VR can facilitate social interactions among fans, allowing them to share experiences and engage with one another in virtual environments. This social aspect of VR enhances the overall fan experience, making it more communal and engaging.
Advantages of Virtual Reality in Sports Training
The advantages of incorporating virtual reality into sports training are manifold. One of the most notable benefits is the ability to conduct risk-free practice sessions. Athletes can engage in high-intensity drills without the fear of injury that often accompanies physical training.
This is particularly beneficial for contact sports where injuries are common. By practicing in a virtual environment, athletes can hone their skills while minimizing physical strain. Another significant advantage is the ability to analyze performance data in real-time.
Many VR training systems come equipped with analytics tools that track an athlete’s movements and decision-making processes during simulations. Coaches can review this data to identify areas for improvement and adjust training regimens accordingly. For instance, a soccer coach might analyze a player’s positioning during a simulated match to provide targeted feedback on defensive strategies.
This data-driven approach enhances the effectiveness of training programs and leads to more informed coaching decisions.
Challenges and Limitations of Virtual Reality in Sports
Despite its numerous advantages, the integration of virtual reality into sports training is not without challenges. One major limitation is the cost associated with implementing VR technology. High-quality VR systems can be expensive to purchase and maintain, which may deter some teams or organizations from adopting this innovative approach.
Additionally, there is a learning curve associated with using VR technology effectively; both athletes and coaches must invest time in becoming proficient with the systems. Another challenge lies in the potential for over-reliance on virtual training at the expense of real-world practice. While VR provides valuable simulations, it cannot fully replicate the unpredictability and physicality of actual competition.
Athletes may become accustomed to the controlled environment of VR training and struggle when faced with the dynamic nature of live games. Striking a balance between virtual training and traditional methods is essential to ensure that athletes remain well-rounded and prepared for real-world challenges.
Future Potential of Virtual Reality in Sports

The future potential of virtual reality in sports is vast and exciting. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated applications that enhance both training and fan engagement. For instance, developments in haptic feedback technology could allow athletes to feel realistic sensations during VR training sessions, further bridging the gap between virtual practice and real-life performance.
This could lead to more effective skill acquisition as athletes develop muscle memory through immersive experiences. Moreover, as VR becomes more accessible and affordable, we may see its widespread adoption across various levels of sport, from youth leagues to professional teams. This democratization of technology could lead to a new generation of athletes who are trained using advanced methods from an early age, potentially raising the overall level of competition across all sports.
Additionally, as fan engagement continues to evolve, we may witness innovative uses of VR for remote viewing experiences that allow fans to feel as if they are part of the action, regardless of their physical location.
Virtual Reality in Sports Marketing and Sponsorship
Virtual reality is also making waves in sports marketing and sponsorship strategies. Brands are increasingly leveraging VR technology to create immersive advertising experiences that resonate with consumers on a deeper level. For example, companies can develop interactive VR campaigns that allow fans to experience their products in action during sporting events or engage with athletes in unique ways.
This not only enhances brand visibility but also fosters emotional connections between consumers and brands. Sponsorship opportunities are also evolving with the integration of VR technology. Brands can sponsor virtual experiences that allow fans to engage with their products or services in innovative ways during events or through team apps.
For instance, a beverage company might create a VR experience where fans can virtually participate in a post-game celebration with players while enjoying their product. Such initiatives not only enhance brand loyalty but also create memorable experiences that resonate with consumers long after the event has concluded.
The Impact of Virtual Reality on the Future of Sports
The impact of virtual reality on the future of sports is profound and multifaceted. As this technology continues to evolve, it promises to reshape how athletes train, how fans engage with their favorite teams, and how brands connect with consumers. The potential for enhanced performance through realistic simulations and data-driven insights is immense, while the opportunities for immersive fan experiences are boundless.
As we look ahead, it is clear that virtual reality will play an increasingly central role in the sports industry. The challenges associated with its implementation will need to be addressed, but the benefits far outweigh these obstacles. With ongoing advancements in technology and growing acceptance within the sports community, virtual reality is poised to redefine what it means to train, compete, and engage with sports in ways we have yet to fully imagine.
For those interested in how technology is reshaping various industries, a related article worth reading discusses the future of business and the role of innovation in driving success. This article, available on the Times of Innovation website, explores how emerging technologies, much like virtual reality in sports, are pivotal in transforming traditional business models and enhancing consumer experiences. You can read more about these insights and how they parallel the advancements in sports training and fan engagement by visiting