Solar Bursts Squished Jupiter’s Magnetic Shield, Left Half of the Planet Scorching Hot
In a first, scientists have discovered a massive wave of solar wind that hit Jupiter, squishing its magnetic field and causing the temperature of its upper atmosphere to soar to scorching levels. This unprecedented event sheds light on the complex interactions between the largest planet in our solar system and the powerful forces emanating from the Sun.
The study, led by researchers from the University of Leicester in the United Kingdom and the University of Liège in Belgium, utilized data from the Juno spacecraft to analyze the impact of a solar coronal mass ejection on Jupiter. This event, which occurred in January 2014, unleashed a barrage of energetic particles and magnetic fields towards the gas giant, disrupting its magnetic environment on a scale never seen before.
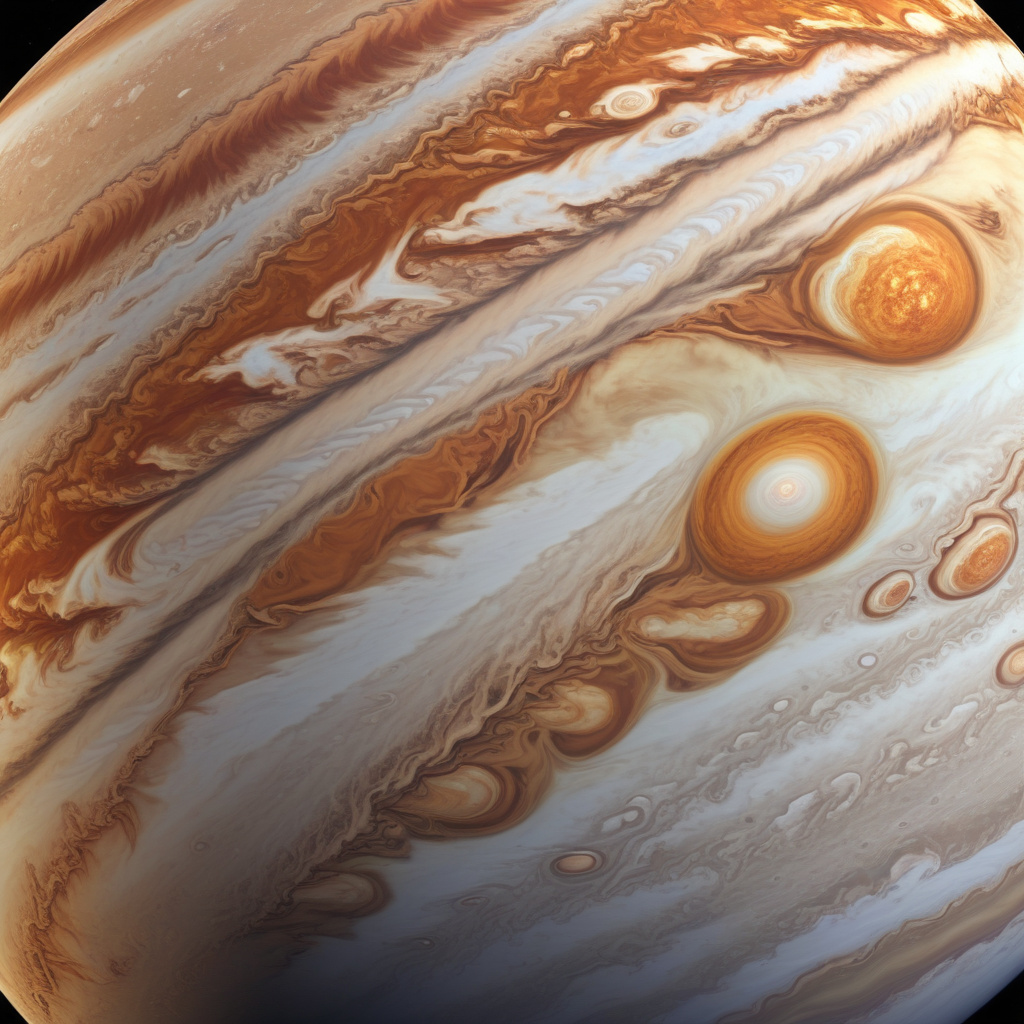
Jupiter’s magnetic field is already immense, stretching millions of kilometers into space and generating intense auroras at its poles. However, when the solar wind slammed into the planet, it compressed this magnetic shield on the dayside, effectively squeezing it towards the surface. As a result, the upper atmosphere of Jupiter experienced a significant increase in temperature, particularly on the side facing the Sun.
The findings, published in the journal Nature Astronomy, provide valuable insights into how solar activity can influence the dynamics of planetary magnetospheres. While Earth is well-protected from such events due to its strong magnetic field and thick atmosphere, gas giants like Jupiter are more vulnerable to the effects of solar storms.
One of the most striking observations from the study was the stark temperature asymmetry between the dayside and nightside of Jupiter. While the dayside experienced a considerable heating effect from the solar wind compression, the nightside remained relatively unaffected. This imbalance highlights the profound impact that external factors can have on the atmospheric conditions of a planet, even one as massive as Jupiter.
The researchers also noted that the solar wind interaction caused Jupiter’s magnetosphere to wobble significantly, akin to a flag flapping in the wind. This dynamic response underscores the complexity of magnetic fields in space and the intricate dance between the solar wind and planetary environments.
Understanding these phenomena is not only crucial for unraveling the mysteries of our own solar system but also for studying exoplanets orbiting distant stars. By examining how solar activity affects giant planets like Jupiter, scientists can gain valuable insights into the potential habitability of other worlds and the factors that shape their climates.
As our exploration of the solar system continues to uncover new wonders and surprises, the interaction between the Sun and its planetary neighbors remains a fascinating area of research. The recent discovery of the solar wind-induced temperature spike on Jupiter serves as a reminder of the dynamic forces at play in our cosmic backyard, shaping the worlds beyond our own.
In the vast tapestry of the universe, each planetary interaction offers a glimpse into the intricate mechanisms that govern celestial bodies and the awe-inspiring phenomena that unfold in the depths of space. The solar bursts that squished Jupiter’s magnetic shield are but one chapter in the ongoing saga of discovery and exploration that defines our quest to understand the cosmos.
solar wind, Jupiter, magnetic field, planetary magnetosphere, solar system