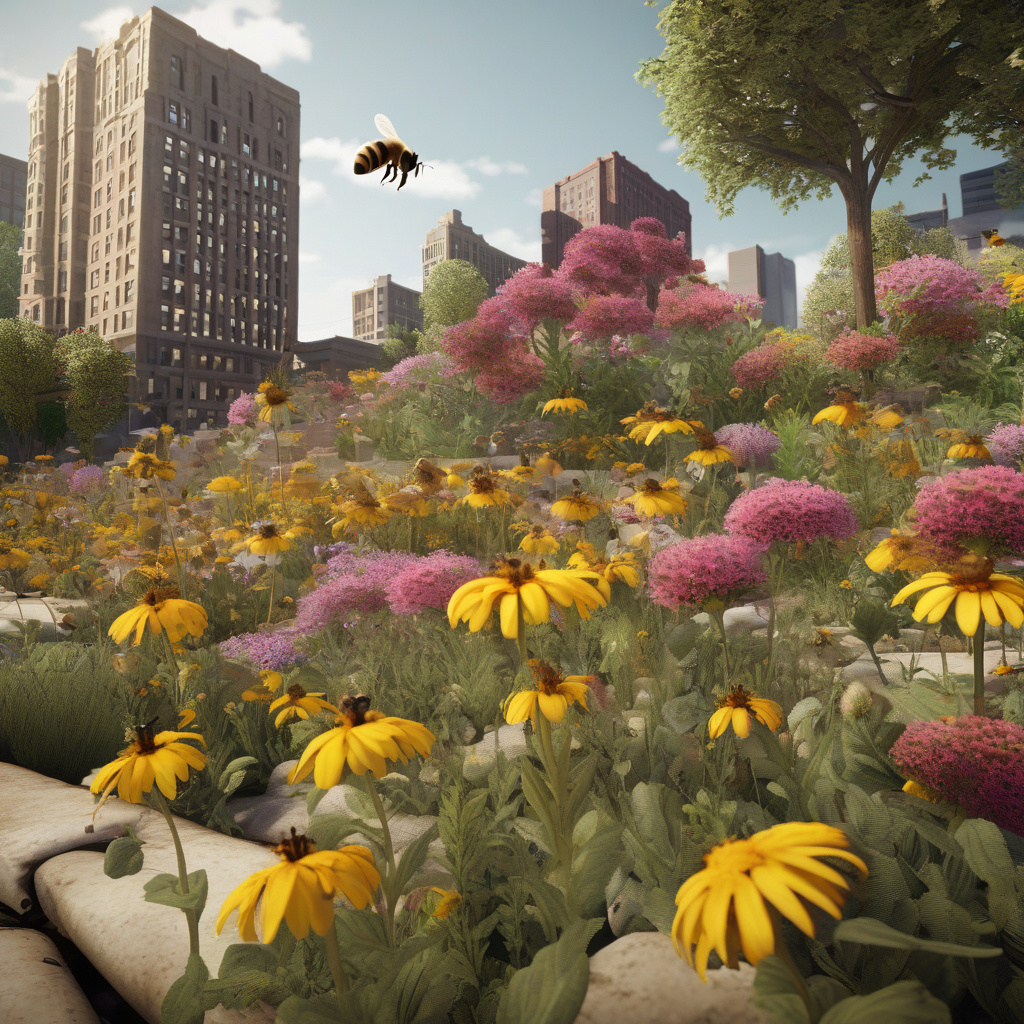
Study Finds 65% Decline in Urban Bee Population: Heat and Land Use Are Main Culprits
Across the globe, the diversity of insect species and their populations are falling rapidly. A recent study has highlighted a concerning trend in urban areas, revealing a significant 65% decline in the bee population. This alarming discovery sheds light on the detrimental effects of urbanization, climate change, and land use practices on essential pollinators.
The decline in the urban bee population is a critical issue that demands immediate attention and action. Bees play a crucial role in pollinating plants, including many of the fruits, vegetables, and nuts that humans consume. Without bees, our food supply and ecosystem health are at risk. Understanding the factors contributing to this decline is essential to implementing effective conservation strategies.
One of the primary culprits behind the decline in urban bee populations is the increasing heat in cities. Urban heat islands, created by the abundance of concrete and asphalt surfaces that absorb and retain heat, can have devastating effects on bee populations. Bees are highly sensitive to temperature changes, and excessive heat can disrupt their foraging patterns, nesting behaviors, and overall health.
Additionally, land use practices in urban areas are contributing to the decline in bee populations. The widespread use of pesticides and herbicides in urban landscaping can be toxic to bees and other pollinators. Loss of habitat due to urban development, deforestation, and monoculture landscapes further exacerbates the challenges that bees face in finding food, shelter, and nesting sites.
To address the decline in urban bee populations, concerted efforts are needed at the local, regional, and global levels. Cities can adopt bee-friendly policies and practices, such as creating pollinator-friendly green spaces, reducing pesticide use, and promoting native plantings. Community engagement and education programs can raise awareness about the importance of bees and empower individuals to take action to protect them.
Innovative solutions, such as green roofs, vertical gardens, and urban beekeeping initiatives, can help create more sustainable urban environments that support bee populations. Collaborations between government agencies, conservation organizations, businesses, and community groups are essential to implementing holistic approaches to bee conservation.
Furthermore, addressing the root causes of urban bee population decline requires a multifaceted approach that considers the interconnectedness of environmental, social, and economic factors. Sustainable urban planning, biodiversity conservation, and climate change mitigation efforts are integral to creating healthier and more resilient ecosystems for bees and other pollinators.
As we grapple with the urgent need to reverse the decline in urban bee populations, we must recognize that the fate of bees is closely intertwined with our own well-being. By taking concrete actions to protect and support bee populations, we can safeguard biodiversity, food security, and environmental sustainability for future generations.
#bees, #urbanization, #pollinators, #climatechange, #conservation