O2’s 3G Switch-Off: A £13m Electronic Waste Dilemma
In a move towards technological advancement, O2’s decision to switch off its 3G network by 2025 is poised to bring about a concerning consequence – the generation of approximately £13 million worth of electronic waste. This decision, while reflective of the ever-evolving landscape of telecommunications, raises critical questions about the environmental impact of such a shift.
The phasing out of 3G technology by O2, a prominent player in the telecommunications industry, signifies a significant step towards paving the way for 5G networks, which promise faster speeds and enhanced connectivity. However, the aftermath of this transition poses a pressing challenge in terms of managing the electronic waste that will be generated as a result.
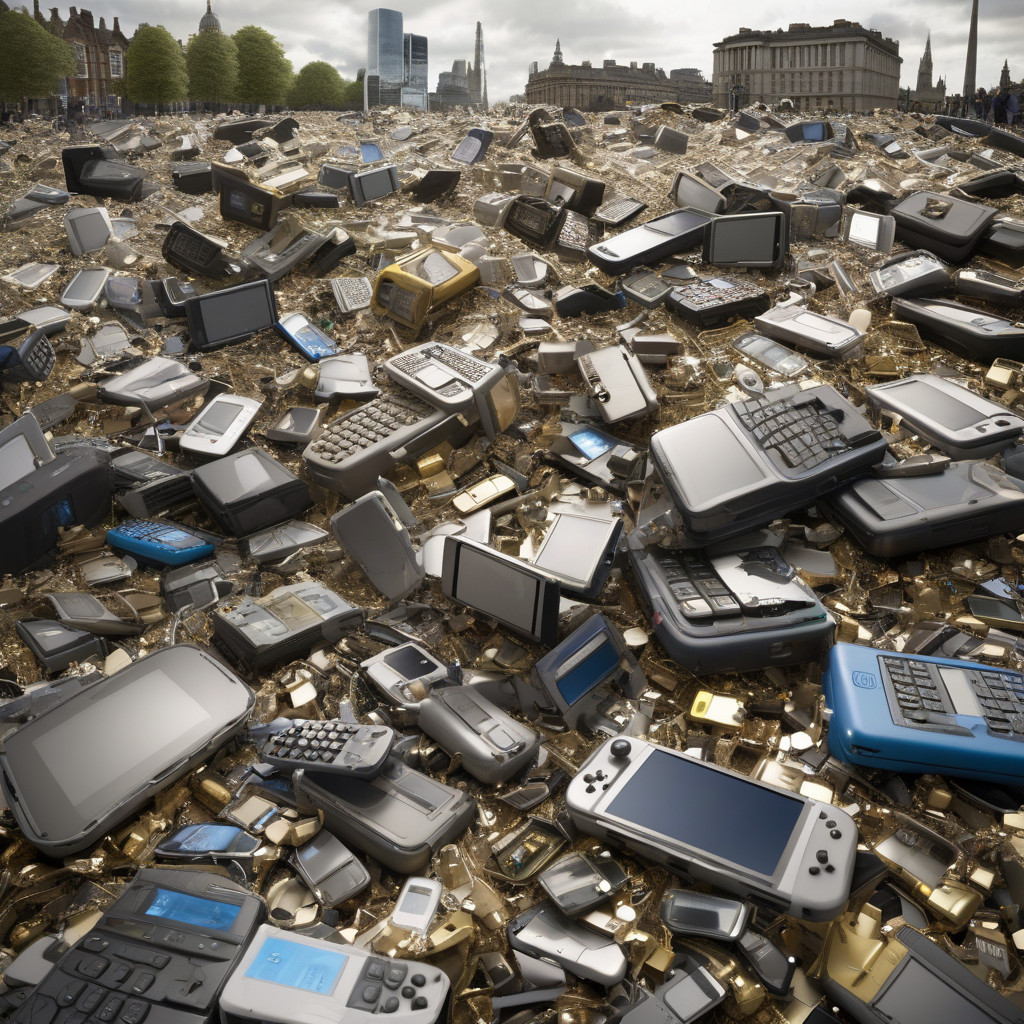
Electronic waste, or e-waste, encompasses a wide range of discarded electronic devices, including smartphones, tablets, and routers. With the impending switch-off of the 3G network, a surge in obsolete devices is expected, contributing to the growing e-waste epidemic. According to projections, the value of this discarded electronic equipment could amount to a staggering £13 million, underscoring the magnitude of the issue at hand.
The environmental repercussions of e-waste are profound and multifaceted. Improper disposal of electronic devices can lead to toxic substances leaching into the soil and water, posing risks to both human health and the environment. Additionally, the sheer volume of electronic waste generated contributes to landfill overcrowding and further exacerbates resource depletion.
To address the challenges posed by the impending influx of electronic waste resulting from O2’s 3G switch-off, proactive measures need to be taken. Recycling presents a viable solution to mitigate the environmental impact of e-waste accumulation. By recycling old electronic devices, valuable materials such as copper, gold, and silver can be recovered and reused, reducing the strain on natural resources and curbing the need for new raw materials.
Furthermore, raising awareness about the importance of responsible e-waste management is crucial in fostering a culture of sustainability. Encouraging consumers to recycle their old electronic devices through designated e-waste collection points or recycling programs can help divert electronic waste from landfills and promote a circular economy approach.
In conclusion, while O2’s 3G switch-off represents a strategic move towards technological innovation, it also underscores the urgent need for sustainable e-waste management practices. By recognizing the environmental implications of electronic waste generation and taking proactive steps to recycle and repurpose old devices, we can work towards minimizing the environmental footprint of technological advancements.
Ultimately, the transition to 5G technology should not come at the expense of environmental sustainability. It is imperative for stakeholders across the telecommunications industry to collaborate on effective e-waste management strategies to ensure a greener and more sustainable future for all.
#O2, #3G, #ElectronicWaste, #Recycling, #Sustainability